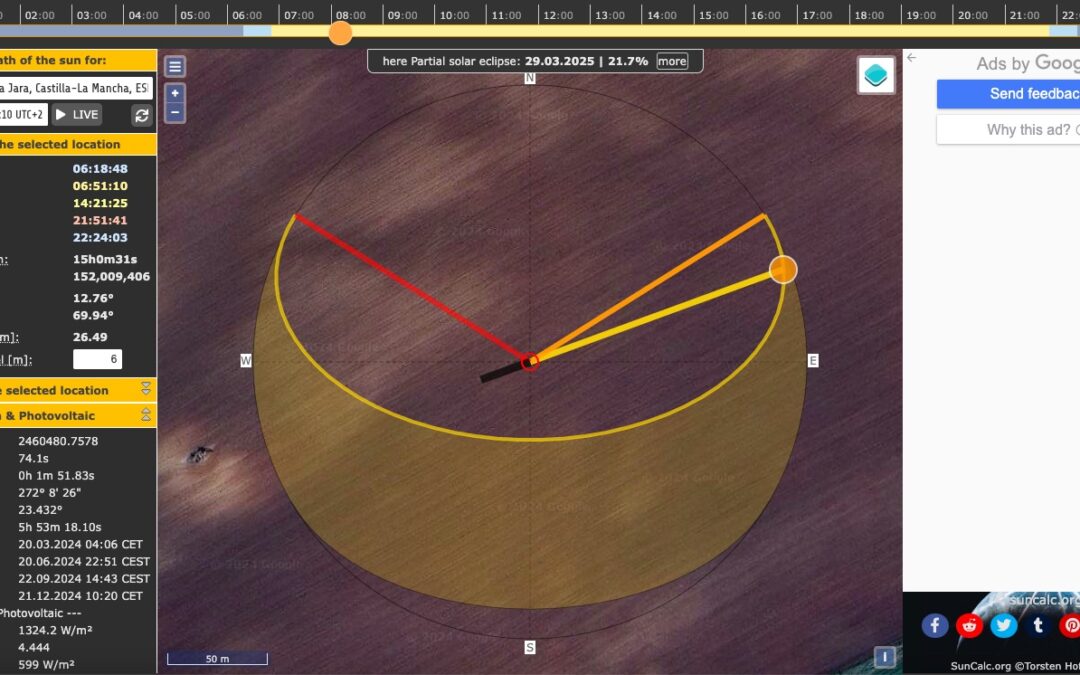
I start this article to explain briefly the information that appears in the page www.suncalc.org of which I put a screenshot of what you will find when you start.
From there, at any point on the map you can set the location you want to mark, and where you want to get the data from.
The following is an example of a photo of a place near Madrid, which I will describe below, so that you can easily adjust it to your location.
SOLAR DATA FOR THE SELECTED LOCATION
The following data are displayed
Dawn : Dawn time
Sunrise: Time for sunrise
Culmination: Time when the sun is at its highest point in the day.
Sunset: Time of sunset
Dusk: Time of day when it is dark.
Daylight duration: Time of day
Distance km: Distance from the sun to the point we mark on the map.
Shadow length [m]: Indicates the meters of shadow that an object will give, at the point you mark.
On the map it is marked by a black line that starts where you mark the object.
At an object level [m]: To indicate the height of the object you want the shadow to be displayed.
Solar azimuth is the angle formed by the south direction with the horizontal projection of the sun, to the north by the northeast or northwest.
This value is decisive at the time of placing the solar panels to receive the maximum solar radiation and the greenhouses to find out the optimal angle of incidence of radiation, in case we have the option or want to modify the angle of the roofs or walls.
Air mass, (AM) as the quotient between the optical path of a solar ray and that corresponding to the normal to the earth’s surface (zenith angle zero) and which is related to the solar height (α).
GEODATA FOR THE SELECTED LOCATION
The coordinates of the location in the two reference systems appear, as well as the height at which it is with respect to the sea, the point that we mark on the map.
MORE SOLAR DATA & PHOTOVOLTAIC
This section is indicated for the placement of solar panels, repeats location values and reminds us of the days and times when the Spring Equinox (Mar Equinox) and Autumn Equinox (Sep Equinox) occur, as well as the two Summer Soltice (Jun Solstice) and Winter Soltice (Dec Solstice).
Already in the PHOTOVOLTAIC subsection,
Solar Constant : Solar constant is a practically fixed value for the whole earth, which is around 1361 W/mw.
But there are some values that are very valid for those who keep plants outdoors or in greenhouses,
Air Mass : Literally air mass, and the more perpendicular the sun is to the earth’s surface, the shorter the distance that solar radiation travels through the atmosphere, and at this distance, the more air mass is generated.
Thus air mass is the coefficient between the path of this radiation, expressed in light, with respect to the horizontality of the earth taking this as zero, all this is related and varies according to the solar height.
Everything written refers to the sun and its light.
And although it is clear that it is a value to take into account it is necessary to develop other concepts to know which is the best light that we can offer to our plants and how, in the different times of the year.